Land accounting
In the context of the development of Land Cover Classification System, the Food and Agriculture Organization and the United Nations Environmental Programme define land use as "characterised by the arrangements, activities and inputs people undertake in a certain land cover type to produce, change or maintain it".
Land use information relates to the geographic location and extent of the spatial unit under consideration, the purpose of activities undertaken, their temporal aspects and the technologies employed (e.g. fertilizer, irrigation...). Quantitative measures such as those related to areas and products prove useful to understant and manage the reasons and incentives underlying the current land use and its future development (e.g. land tenure, labour costs, market conditions...). Agricultural land-use data are important for the validation of agricultural land evaluation, for early warning for food security; natural disaster relief operations; farming systems and policy formulation, for example in relation to sustainable resources use. (1)
For urbanised regions, the use of land and its value, depend on the infrastructural network that serves specific area: electricity, water supply, communication and transportation systems are key assets to consider when valuing land. In urban areas there are relatively small spatial ownership possibilities and a high rate of change in land ownership and use. Cities grow fast and authorities have to deal with the associated costs of providing urban infrastructures. (2)
Land use regulation and practices are very well established but land monitoring is becoming insufficient if not integrated into urban and regional planning. Land supply and capacity monitoring involves measuring, analysing and evaluating land availability and its capacity to accommodate for further development.
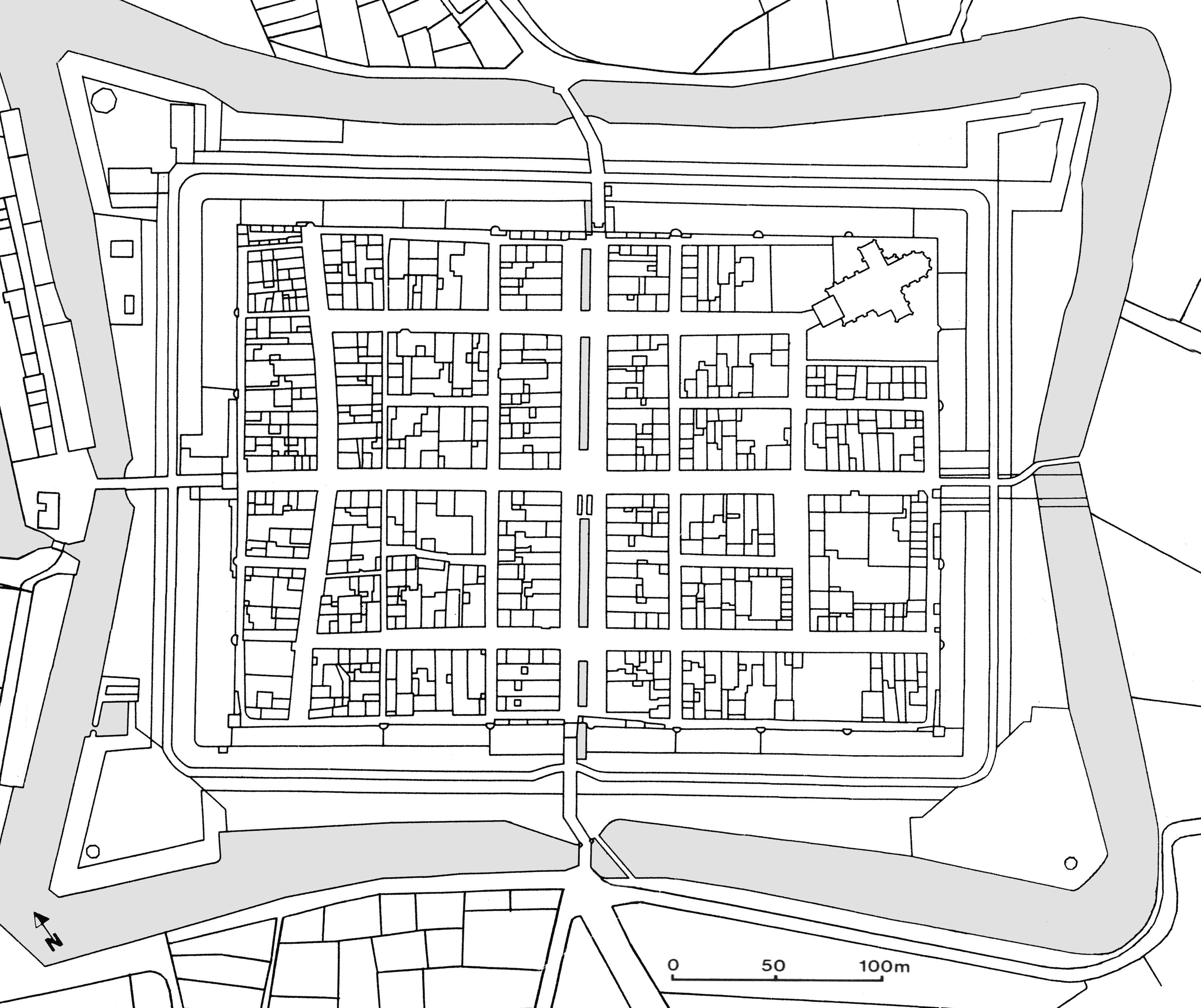
Example of cadastral plan.
The tax-lot parcel is a basic building block of land information systems, a parcel being defined as the smallest unit of geography that can be managed and controlled by one person or entity; it corresponds to real-world transactional activity related to urban land.
Geographic Information Systems have been used for long time to monitor land use. Satellite images prove to be very useful in the generation of action plan maps, in the framework of intelligent cadastral vector data. Thematic and action plan maps may be enriched in details and land cover changes detection can be performed through processing procedures and implemented in GIS.
National governments are usually responsible for cadastral mapping which constitutes an official record of land subdivisions, facilitating land ownership procedures and assisting in the valuation and taxation of land. Satellite high resolution data are very useful for an efficient and unbiased property mapping (3).
References
(1) FAO Land Resources, http://www.fao.org/nr/land/use/en/
(2) Moudon A. V. and Hubner M. 2000. Monitoring Land Supply with Geographic Information Systems.
(3) http://www.satimagingcorp.com/applications/engineering-and-construction/cadastre_and_land_records/
Products | Source | Descriptions | Product Standards | Ref. Project |
|---|---|---|---|---|
soil sealing |
|
|
| |
urban audit |
|
| urban atlas | |
general land cover |
|
| land use resources monitoring | |
| Urban Atlas | Copernicus Land Monitoring services | |||
land use and quality: urban zone maps |
| controlling land take and the preservation of urban green spaces |
|
|
| land use and quality: land use change characterisation | Land use maps describe not only the physical characteristics of the Earth’s surface (land cover), but also the actual anthropogenic usage on the ground. The product differentiates basic land cover types (e.g. built-up areas) into different use classes, such as residential areas, industrial complexes, roads, buildings, or cropland. |
Topic | Description | Keywords | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
Urban Atlas |
|
|
|

This page has no comments.