Land use studies
Land is both a natural and an economic resource. It is the basis of natural ecosystems and biodiversity and it plays a crucial role in the carbon cycle. Moreover plenty of human activities rely on its services, from agriculture and forestry, to transport, housing and other industries and services.
According to Eurostat (1)
- Land cover refers to the bio-physical coverage of land (e.g. crops, grass, broad-leaved forest, or build-up area),
- Land use indicates the socio-economic use of land (e.g. agriculture, forestry, recreation or residential use).
Data on agricultural land-use are valuable for conducting studies on a various perspectives concerning agricultural production, food security and for deriving cropping intensity among others uses. Indicators derived from the land-use categories can also elucidate the environmental sustainability of countries’ agricultural practices. Land use information are significant for: understanding the structure of a country’s agricultural sector; making economic plans and policies for food security; deriving environmental indicators, including those related to investment in agriculture and data on gross crop area and net crop area which are useful for policy formulation and monitoring. (2)
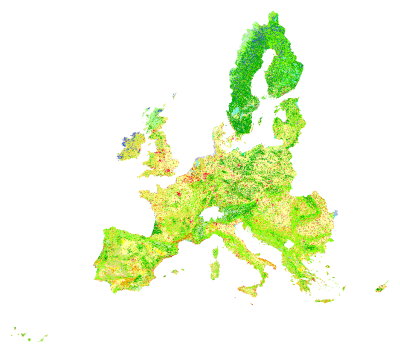
Corine Land Cover 2000
Land cover/use data also form the basis for spatial and territorial analyses which are increasingly crucial for policy planning in many respects. The use of sophisticated land information systems allows planners to enlarge the scope of their analysis from land use and zoning to causal relationships between land utilisation, land and infrastructure development, fiscal impacts and market forces. Land-use planning means the systematic assessment of physical, social and economic factors in such a way as to encourage and assist land users in selecting options that increase their productivity, are sustainable and meet the needs of society.
One example of the use of satellite imagery for statistical purposes is Corine Land Cover, part of the European Union CORINE project (3). In the CORINE system, information on land cover and changing land cover is directly useful for determining and implementing environment policy and can be used with other data (on climate, inclines, soil, etc.) to make complex assessments (e.g. mapping erosion risks). The benefits of using a single joint project to meet both European Community and national (or even regional) needs considerably influenced the general features of the land cover project: scale, area of the smallest mapping unit and nomenclature.
Earth observation satellites facilitate the compilation of land cover inventories of wide geographical areas in short time. Acquired data are available on a regular basis for all points on the globe (even if optical data still suffer from cloud cover issues), making it easier to categorise and map land cover and use even in small areas and to make comparisons between different countries.
References
(1) http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/portal/page/portal/lucas/introduction
(3) http://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/COR0-landcover
(4) http://land.copernicus.eu/

This page has no comments.