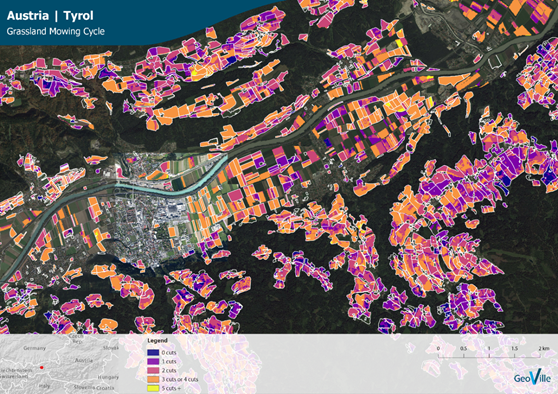
Example for mowing cycle in Tyrol, Austria (Source: GeoVille) | ||||||||||
Category | ||||||||||
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION | ||||||||||
The cutting (here: mowing) moving of managed grassland to produce hay for livestock feed represents a major part of the total agricultural production in some regions. Therefore, it is valuable to monitor which areas of grassland are mowed to get information about hay production, and also how many times they are mowed in a growing season. The frequency and timing of mowing can also be used as evidence for possible damages on grasslands and monitoring the overall grassland productivity. Reliable long-term data on grassland productivity and mowing cycles is used in agricultural insurance for development of index-based products for grasslands and pasture lands, monitoring grassland insurance portfolio by underwriters and assessment assessing the scale and character of damage in loss adjustment. Detailed information on grassland mowing cycle is an important service for all major stages of the product cycle (product development, risk pricing, underwriting, loss assessment, claim settlement). With grasslands mowing data agro-insurers are able to monitor the full cycle of the livestock fodder production. | ||||||||||
PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS | ||||||||||
Main processing stepsThe methodology of the automatic cut detection and counting algorithm is based on an analysis of optical and radar satellite imagery analysing temporal profiles over grassland parcels. It is based on a combination of various vegetation indices such as the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) and multiple stages of cluster analysis. Analysis is based on a pixel-by-pixel computation considering administrative or other boundaries. | ||||||||||
Input data sourcesOptical: Sentinel-2 Radar: Sentinel-1 Supporting data: n.a. | ||||||||||
Spatial resolution and coverageSpatial resolution: 10m Coverage: Regional/national level (macro); Watershed/agro-ecological level (meso) Availability: globally available | ||||||||||
Accuracy / constraintsThematic accuracy: > 85 % Spatial accuracy: Absolute geolocation is constantly monitored for S2A and S2B. The long-term performance is close to 11 m at 95% for both satellites. | ||||||||||
LimitationsLong-time gaps between observations due to cloud cover can make it impossible to detect cut events directly. Remaining noise (e.g. due to undetected clouds) could also result in false identifications of cutting events. | ||||||||||
Frequency / timelinessFrequency: upon request – across growing season, within-season, annual, multi-annual Timeliness: near real-time | ||||||||||
Delivery / output formatData type: GIS-ready data formats; Raster; API (depending on customer needs) File format: GeoTIFF, ESRI Grids, others on request (depending on customer needs) | ||||||||||
AccessibilityCommercially available on demand from EO service providers. | ||||||||||
CHALLENGES ADDRESSED - USE CASE(S) | ||||||||||
Product Development: Product Sales:
Underwriting:
Loss Adjustment:
Claims Handling: | ||||||||||
...